National
Taxonomy Term List
Advancing Albania’s planning for medium and long-term adaptation through the development of a National Adaptation Planning (NAP) process
This project is designed to help the Government of Albania increase its capacity to address the country’s climate change vulnerabilities by supporting the development of a national plan for climate change adaptation. The support focuses on 1) strengthening the national mandate, strategy and steering mechanism for assessing and addressing capacity gaps (particularly in the priority sectors of tourism, urban development, agriculture, transport, and energy); 2) develop a National Adaptation Plan (NAP) Strategy action plan and implementation plan, and 3) develop financing, monitoring and evaluation strategies to ensure that capacities and funding options are institutionalized for the long-term sustainability of adaptation planning beyond the life of the project.
With financing from the Green Climate Fund, the project "Advancing Albania’s planning for medium and long-term adaptation through the development of a National Adaptation Plan (NAP) process" is supporting the Government of Albania to increase its capacity to address the country’s climate change vulnerabilities.
Albania’s primarily rural population is highly vulnerable to the effects of climate change, where extreme rain events frequently result in destructive flooding, while agricultural livelihoods and drinking water supplies are threatened during dry periods. As temperatures rise, climate scenarios predict increased severity and frequency of these extreme wet and dry conditions, along with decreasing annual rainfall. These changes place Albania’s population at risk and pose a threat among others to the hydropower and tourism industries.
To address these vulnerabilities, the Government of Albania launched its NAP process in February 2015, with the support of GIZ and UNDP, through consultations with national stakeholders and a stocktaking exercise. A preliminary roadmap for the NAP implementation was formulated and validated by representatives from the Ministry of Tourism and Environment, as well as stakeholders from the Inter-ministerial Working Group on Climate Change (IMWGCC).
The analytical exercises highlighted the existing weaknesses and demonstrated the prevailing barriers to climate change adaptation (CCA) planning in Albania. The results confirmed that to adequately address climate change vulnerabilities, Albania must overcome information gaps, vulnerability assessments, climate adaptation planning capacity weaknesses, and a lack of awareness of CCA – both at national and sub-national levels. In addition, climate change is not integrated into existing environmental and development policies or their associated budget priorities, and financing appropriations for adaptation are absent.
The underlying challenge lies in the lack of a comprehensive framework for adaptation in Albania. The National Communications provide a preliminary assessment of adaptation priorities, while a national NAP Framework Document was developed as part of the NAP preparation and stocktaking process in 2016. To leverage these preliminary activities towards climate resilience, this readiness effort aims to address the weaknesses and barriers identified in the NAP Framework Document.
In September 2021, Albania submitted its National Adaptation Plan, including a comprehensive financing strategy to the UNFCCC.
The project aims at delivering the following results under the three main outcomes:
- Strengthen legal and institutional framework and mandate for climate change adaptation work at the national level;
- Upgrade stocktaking on climate vulnerabilities, adaptation opportunities and development needs and update vulnerability analyses;
- Address adaptation related capacity gaps at national and subnational levels;
- Establish long-term adaptation capacity development methodologies to ensure ongoing skills development and increased awareness of climate change adaptation;
- Formulate NAP Strategy action plan and the accompanying communications plan;
- Promote CCA integration into existing planning and budgeting and cross-sector coordination;
- Develop NAP implementation plan;
- Establish systems to monitor NAP process and adaptation progress;
- Identify options for securing and scaling up financing for adaptation; develop a financing plan.
Project Updates
After the inception workshop in December 2021, the project, in collaboration with stakeholders, established criteria for selecting up to eight municipalities for climate change adaptation roadmaps and identified priority sectors for analysis. UNDP signed a Memorandum of Understanding with Tirana Polytechnic University and the Institute of Geosciences (IGEO) to foster cooperation.
The project also supported the development of a new legal proposal to update the mission of the IGEO to include CCA, as well as the operational manual for the Interministerial Working Group on Climate Change and a draft reporting format for the National Climate Change Committee (NCCC).
Since 2022, the project team has accelerated project implementation, making significant progress in strengthening the institutional framework and capacities for CCA planning. This involved concluding procurement services to implement activities.
Recent successes include the establishment of the NCCC and the finalization of its Operations Manual, the development of a Monitoring, Reporting, and Verification (MRV) system, and progress on legal acts related to the IGEO. Additionally, work was undertaken on climate and socio-economic data analysis, inventory of adaptation projects, capacity assessment at national and subnational levels, and training programs.
In 2023, various stakeholders were engaged and sensitized on the NAP process. Activities have included refining vulnerability and risk assessments, developing a national database for climate change scenarios and sector vulnerability assessment, compiling a regional climate change scenario report, finalizing the expanded stocktaking report organized by priority sectors, and delivering guidelines and screening tools for gender-sensitive CCA planning.
Outcome 1: Institutional and capacity gaps assessed and addressed.
Outcome 2: NAP Strategy action plan finalized and implementation plan in place.
Outcome 3: Financing strategy and monitoring and evaluation for climate change adaptation in medium – to long-term established


Readiness for the National Adaptation Plan Process in Argentina
The project supported the Government of Argentina in establishing its adaptation planning process. This involved identifying gaps, capacity building, and integrating climate change considerations across national, regional, and local levels. By doing so, the project facilitated the assessment and reduction of vulnerability to the adverse effects of climate change by integrating climate change adaptation into the country's development strategies.
The scope of the project included the preparation of the National Adaptation Plan (NAP) with a regional and multi-sectoral approach. Additionally, it involved the development of a system to monitor and assess adaptation needs and measures under the Law 27250 Minimum Standards for Adaptation and Mitigation to Climate Change (Ley de Presupuestos Mínimos de Adaptación y Mitigación al Cambio Climático). To achieve the proposed outcomes, the project developed a communication strategy on climate change adaptation, carried out a series of studies to identify adaptation options, and supported inter-sectoral and inter-jurisdictional collaboration within the framework of the National Cabinet on Climate Change (NCCC), the Federal Environment Council (COFEMA), and the National System for Comprehensive Risk Management (SINAGIR).
In recent years, Argentina has made decisive progress in planning and implementing measures to adapt to climate change. The National Communications on Climate Change have made valuable contributions, such as providing information, conducting diagnoses, and identifying various information gaps. Within the framework of the National Climate Change Cabinet (NCCC) work, several sectoral initiatives that are directly or indirectly related to climate change adaptation were identified, as well as other information and capacity needs.
This project, funded by the Green Climate Fund (GCF) NAP Readiness Programme, aimed to deepen this work by supporting National Adaptation Plan (NAP) development. This involved facilitating the evaluation and reduction of vulnerability to the adverse effects of climate change by integrating climate change adaptation into Argentina’s development strategies.
The “Readiness for the National Adaptation Plan Process” project was launched in March 2019 to support Argentina’s efforts to assess and reduce climate change vulnerability by integrating climate change adaptation into the country's sustainable development. To achieve this goal, the project aimed to build adaptive capacity and resilience. It sought to integrate climate change adaptation into both new and existing policies, programmes, activities, and development planning processes and strategies across relevant sectors at different levels.
In particular, the project supported the Government of Argentina to:
1) Establish a national process to coordinate adaptation planning at all relevant scales with a medium and long-term perspective.
2) Identify capacity gaps and strengthen capacities for adaptation planning and implementation, integrating adaptation to climate change into national, provincial, and municipal development planning processes.
3) Support the preparation of the NAP with a regional and multi-sectoral approach in the framework of the National Climate Change Cabinet.
4) Establish a system for monitoring and assessing needs and adaptation measures.
5) Design a communication strategy on adaptation to climate change, focusing on the most vulnerable populations and improving climate information services; and
6) Support inter-sectoral and inter-jurisdictional collaboration within the framework of the National Cabinet on Climate Change.
In most of non-Patagonian Argentina, the average temperature has increased up to half a degree between 1960 and 2010, with smaller increases in the center of the country. These changes have already affected natural and human systems, and according to climate projections, impacts will intensify. More frequent and intense rainfall has resulted in more frequent floods, while dry winter periods have become longer in the west and north of the country. This has adversely affected water availability for some populations, increased the risks of grassland fires, and caused livestock stress.
Argentina has committed to addressing climate change adaptation systematically and inclusively through actions and initiatives articulated in its National Adaptation Plan, its 2016 National Determined Contribution (NDC), and it’s second NDC in 2020. The NDCs and further work implemented within the framework of the National Cabinet on Climate Change detected various information gaps and sectoral initiatives that are directly or indirectly linked to climate change adaptation. The project focused on addressing these identified gaps, including establishing a baseline for the country's adaptation situation and initiating a participatory planning process.
The project goals were achieved through three main outcomes and their corresponding activities.
Outcome 1: Institutional strengthening and coordination for the formulation and implementation of the NAP process
Activities under this outcome focused on initiating the NAP process at the national level under the framework of Law 27250 and focused on strengthening governance and institutional coordination for adaptation planning. This involved developing an appropriate strategy and relevant institutional arrangements and support, such as the formalization of the External Advisory Council through consultation with representatives of civil society organizations, political parties, academia, and Indigenous people, and setting clear groundwork. The strategy outlined clear responsibilities for government ministries and departments, specified milestones and expected outputs of the NAP process, and improved coordination and cooperation mechanisms. The approach included participatory and inclusive approaches with Indigenous communities and others to identify climate risks, impacts, and subsequent mitigation strategies. This extended to the participatory formulation of the National Adaptation Plan and support for provinces in developing Subnational Response Plans. Regulatory support further strengthened the National Climate Change Cabinet, which approved the National Plan for Climate Change Adaptation and Mitigation.
Outcome 2: Awareness raising and capacity building
This outcome built capacities to reduce vulnerability to climate change and facilitate the integration of adaptation into development. A comprehensive education, awareness, and communication strategy in climate change adaptation was created encompassing various components, such as education, awareness, access to public information, citizen participation, culture, and international cooperation. A national-level social perception study facilitated the elaboration of this strategy and evaluated audience needs and preferences. Moreover, the Climate Risk Maps Platform (SIMARCC) was updated, functioning as an interactive tool that identifies climate change risks by illustrating communities and ecosystems with the highest socio-environmental vulnerability.
Training was conducted to promote the evaluation, planning, and implementation of adaptation measures. Workshops and training sessions strengthened subnational climate teams, equipping officials at that level with the necessary tools for the development of adaptation plans. Furthermore, private sector engagement was catalyzed through the launch of the Climate Action Agreement with the Private Sector. This aimed to facilitate collaboration between public and private sectors to achieve Argentina’s climate commitments through a platform for exchange and continuous training.
Outcome 3: Baseline definition; formulation of NAPs; implementation, monitoring and reviewing
Outcome 3 involved broad climate risk analyses identifying ‘adaptation deficits.’ This included vulnerability assessments at specific planning levels within the national context that can inform impactful adaptation solutions.Various studies were conducted on topics such as transport supply chains, regional economies, social vulnerability, economic impacts of climate change, health, and cultural heritage to facilitate risk analysis and identify adaptation options. The project also supported the elaboration of provincial adaptation plans by hiring individual consultants to strengthen the provincial climate teams. Risks and needs at the regional level were identified following economic loss estimates and sector-specific damage assessments.
In collaboration with provincial teams and civil society, a multi-criteria analysis tool was developed to prioritize adaptation measures within the NAP. Measures were prioritized based on their contribution to short- and long-term sustainable socioeconomic development, costs, effectiveness, and efficiency at national and subnational levels. Additionally, efforts were made to identify existing adaptation initiatives within national government areas. Moreover, a strategy for implementing and monitoring the NAP, involving priority measures, was developed. This included the design of the NAP monitoring, evaluation, and learning (MEL) system.
Outcome 1: Institutional strengthening and coordination for the formulation and implementation of the NAP process.
Outcome 2: Awareness raising and capacity building.
Outcome 3: Baseline definition, formulation of NAPs, implementation, monitoring and reviewing.


National Adaptation Plan to advance medium and long-term adaptation planning in Armenia
With financing from the Green Climate Fund, the 'National Adaptation Plan (NAP) to Advance Medium and Long-term Adaptation Planning in Armenia' project supported the Government of Armenia in formulating a national plan for climate change adaptation. Through an iterative process, the project focused on strengthening foundational capacities with the aim of institutionalizing them for long-term sustainability.
The project aimed to address existing barriers, facilitate the prioritization of climate change adaptation investments in priority sectors—such as water resources, agriculture, energy, health, tourism, and human settlement—and increase the identification of financing options. Through the development of the NAP process, Armenia laid the groundwork for the systematic and iterative identification of medium- and long-term risks. The country not only established adaptation priorities but also designed specific activities to ensure that no one is left behind in its efforts to achieve the goals outlined in the Paris Agreement and the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
In tandem with the localization of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), the NAP process contributed to the formulation of corresponding national climate-responsive indicators and targets.
The Government of Armenia launched its national stakeholder consultations for the national adaptation plan (NAP) process in June 2016. A preliminary action plan for NAP implementation was formulated during the stocktaking exercise and approved by the representatives of key sectors and the Ministry of Nature Protection. The government recognizes the NAP process as a key step to achieving the adaptation objectives of its 2015 Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC).
The NAP seeks to address the main challenges to the integration of climate change adaptation into national, sectorial, and local government planning and budgeting, as identified in the 2016 stakeholders' consultations and the NAP Stocktaking report. Focus has been given to strengthening foundational capacities for adaptation and ensuring that they are institutionalized for long-term sustainability (beyond the life of the project). It was expected that at least two NAP iterations would be required for a complete and comprehensive mainstreaming of climate change adaptation into the national development framework and into the development plans of all sectors.
NDCs and NAPs
Armenia’s vulnerability to climate change requires greater investments and integration of climate change adaptation and disaster risk reduction. In 2016, the government began discussions regarding the NAP process through national consultations and a rapid stocktaking exercise. This stocktaking provided a qualitative assessment of the institutional framework and capacities relevant to the NAP process.
The NAP is fully aligned with the adaptation component of the NDC and is recognized as a pivotal element in establishing a constructive feedback loop between Armenia's national and international decision-making on climate change.
By embarking on the NAP process, Armenia laid the groundwork for a systematic and iterative identification of medium- and long-term risks, climate change adaptation priorities, and specific activities aimed at fostering climate adaptive and resilient growth in key sectors. This shift from ad-hoc, project-based approaches to a more coherent and strategic climate change adaptation approach, integrated with the implementation of the Paris Agreement, the Sendai Framework, and the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, positions Armenia to achieve a lasting paradigm shift in reducing the climate risks it faces.
Stakeholder Consultations
As an integral part of the NAP process, a comprehensive stakeholder communication and engagement plan, including a gender action plan, was developed. This plan aimed to ensure broad consultation and involvement of diverse stakeholders at all stages of the NAP. Outreach encompassed sensitization, consultations, and training workshops, tailored to meet stakeholders' specific needs for successful implementation. The overarching goal of these engagement activities was to enhance stakeholder ownership, raise awareness, and bolster knowledge regarding the crucial role of climate adaptation in addressing climate change impacts for sustained, long-term engagement. Stakeholders spanned government institutions, financial and technical partners, international and national non-governmental organizations, and local civil society.
Results
Key project achievements include:
Improved Legislative and Policy Frameworks:
- Integration of climate change considerations into governance mechanisms through the National Action Program of Adaptation to Climate Change and the List of Measures for 2021-2025.
- Updates to the structure, mandate, functions, and rules of procedures of the Inter-agency Coordination Council on Climate Change.
- Formation of three permanent working groups supporting the Inter-Agency Coordination Council.
Integration into Legal Instruments and Sector Strategies:
- Amendments to the Water Code addressing climate change risks, vulnerability, adaptation, and water use permit allocation.
- Draft amendments to the Environmental Impact Assessment law to consider climate change-related risks.
- Development and approval of the "2022-2026 Climate Change Adaptation Plan in the Water Resources Sector."
Territorial Governance Improvement:
- Climate risk and vulnerability assessments and adaptation plans for two regions (Tavush and Shirak) and Yerevan city.
- Development and acceptance of guidelines for climate change adaptation planning at the local and regional levels.
Sector Governance Enhancement:
- Revision of irrigation norms in Ararat Valley with recommendations for replication.
- Updates to River Basin Management Plans for the Southern and Ararat River Basin districts.
- Recommendations on institutional arrangements for mudflow risk management.
- Various assessments, including economic cost-benefit analysis and feasibility studies for reservoirs.
Capacity Building, Awareness, and Education:
- Development of guidelines on urban green infrastructure, landslide risk assessment, and climate change adaptation in agriculture.
- Stakeholder communication and awareness strategy.
- Organizing over 90 workshops, trainings, and public events involving more than 3,200 participants.
- Numerous media interviews and stakeholder roundtable discussions initiated.
NAP Process Continuity:
- Assessment and strategy for private sector engagement in climate change adaptation to strengthen the enabling environment for private sector investments
- Design of water resources and agriculture sectors adaptation concept notes.
- Development of a methodology and guideline for evaluating the NAP process monitoring and evaluation (M&E).
- Establishment of MRV frameworks for climate mitigation and adaptation.
Output 1: Gaps assessed and national mandate, strategy and steering mechanism established
Output 2: Climate evidence and knowledge-base for the compilation of a NAP strengthened
Output 3: NAP implementation facilitated
Output 4: Mechanisms for Reporting, Monitoring and Review of NAPs and adaptation progress in place
Output 5: Funding strategy for the NAP and CCA formulated
The project's first output focuses on identifying information and capacity gaps while enhancing synergies and coordination across sectorial initiatives. This involves strengthening both vertical and horizontal synergies, reducing duplication of effort, and ensuring a more cohesive approach to integrating Climate Change Adaptation (CCA) responses into development planning.
Outputs 2 and 3 aim to bolster institutional, functional, and technical capacities to plan for gender-sensitive CCA. Additionally, the project seeks to enhance the existing climate-related knowledge base for more consistent assessments of climate risks, vulnerabilities, and impacts. The ultimate goal is to improve implementation at both national and local levels.
Output 4 is dedicated to establishing climate change adaptation monitoring capacity. The objective is to efficiently integrate CCA into both national and sectorial planning and management processes.
Output 5 involves the development of a CCA financing strategy. This includes supporting private sector engagement through a comprehensive assessment of the enabling environment and barriers, aligning with Armenia's priorities for private sector development.
Armenia steps up adaptation to the climate crisis (2022)
Possibilities and promotion mechanisms of secondary water use in Armenia discussed with stakeholders (2022)
Video: Climate change adaptation in agriculture in Armenia (2022)
Public hearing on updates of Ararat Basin Management Plan held in the frame of UNDP-GCF NAP project (2022)
Public hearing on updates of Southern Basin Management Plan held in the frame UNDP-GCF NAP project (2022)
"Climate Change and Women in Armenia” awards ceremony announced in the frame of UNDP-GCF NAP project (2022)
Climate change and adaptation awareness raising campaign in the frame of UNDP-GCF NAP project (2021)
RA National Adaptation Plan submitted to UNFCCC Secretariat (2021)
Draft RA water sector adaptation plan presented and discussed in the frame of UNDP-GCF NAP project (2021)
Climate Change challenges and opportunities present in Tavush discussed during a regional visit (2021)
Mudflow risk management in Armenia in the center of attention of the UNDP-GCF NAP project (2020)
UNDP-GCF NAP Project continues raising awareness on climate change adaptation processes (2019)
National Adaptation Plan development process continues in Armenia (2019)
NAP Project Inception Seminar (2019)

National Adaptation Plan (NAP) support project for adaptation planning and implementation in Azerbaijan
Financed by the Green Climate Fund (GCF) this project will support the Government of Azerbaijan (GoA) to facilitate the development of the National Adaptation Plan (NAP) and improve climate change adaptation (CCA) actions in three priority sectors identified by the Ministry of Ecology and Natural Resources (MENR) of the Republic of Azerbaijan through stakeholder consultations: water, agriculture and coastal areas. The NAP readiness support aims to increase climate resilience and adaptation capacity in three priority sectors through the implementation of actions that will reduce or eliminate barriers for an effective adaptation process at the national and local levels.
The primary beneficiaries from this GCF project include the national government, specifically agencies in the three priority sectors, as well as local communities.
The main objective of the “National Adaptation Plan (NAP) support project for adaptation planning and implementation in Azerbaijan” is to increase capacity on climate resilience and adaptation in three priority sectors to reduce or eliminate barriers for an effective adaptation process at the national and local levels.
The Nationally Determined Contributions (NDC) submitted by Azerbaijan in 2017 highlights the need to “develop relevant adaptation measures for decreasing or minimizing the losses that may occur at national, local and community levels per sector.” The priority sectors were identified as water, agriculture and coastal areas. The expected increase in extreme events on the Caspian Sea coastal areas, such as extremely high waves, strong winds and flooding, make those areas particularly vulnerable to climate change and requires the development of targeted adaptation programmes. The stocktaking exercise in 2017 has identified barriers including: a) Limited access to data including limited data exchange by stakeholders in Azerbaijan; b) Insufficient institutional and technical capacity on climate change adaptation at managerial, expert/practitioners and community levels; c) Limited mainstreaming of adaptation in national, regional, local and sectoral planning, budgeting and regulatory framework; d) Limited institutional coordination; and e) Limited monitoring, evaluation and analysis of past and current programmes on climate change adaptation.
This project aims to address the identified barriers and improve adaptation planning in Azerbaijan focusing on three main areas:
- Improve data availability, access and sharing for decision making. The project will establish mechanisms and data solutions to facilitate increased access and sharing of climate and weather information in Azerbaijan, as well as improve the coordination among institutions.
- Enhance institutional and technical capacity for climate change adaptation in water, agriculture, and coastal areas. Limited institutional and technical capacity hinders not only the mainstreaming of CCA considerations into planning processes, but also the implementation of adaptation actions at the national, regional and local levels. A national gender-sensitive CCA capacity building programme will be developed that addresses the gaps in knowledge and capacity of key stakeholders at all levels: from government decision makers and technical personnel, to local communities and the private sector.
- Increase mainstreaming of CCA considerations into planning at national, regional, local levels in the priority sectors. An Adaptation Working Group (AWG) will be established at the national level, a body that will coordinate the development of a NAP Roadmap document. Further planned activities to advance mainstreaming include the development and application of tools (manuals, guidelines) for the inclusion of CCA considerations into sectoral planning, the improvement of the legal framework for adaptation in priority sectors (water, coastal areas, agriculture), the screening, appraisal and accounting of adaptation in public and private investments and the development and implementation of a monitoring and evaluation (M&E) system for adaptation that is compatible with the Strategic Development Road Maps (SDRM) of Azerbaijan.
Project updates
- Comprehensive assessment of existing and needed climate data and vulnerability studies and supplemental CCA vulnerability studies for priority sectors completed.
- Charter for Adaptation Working Group established to coordinate adaptation planning at the national level.
- Climate Vulnerability Index for the country was developed and is available for use. Gender workplan for the project was developed and is used for the project activities.
- Capacity needs assessment for the development of ‘university specialized diplomas and certificates’ for climate change adaptation was conducted.
- The process to develop an online climate change platform is initiated.
- The analyses of the National Legislation on Climate Change was conducted, and the recommendations are being followed-up, including the preparation of new legal documents.
- The series of capacity building and public awareness workshops/seminars for technical personnel and students were organized in the capital as well as in the different regions of Azerbaijan.
- The capacity needs assessment for the decision-makers was conducted and policy briefs were prepared accordingly.
- A workshop, co-hosted by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) and the Ministry of Ecology and Natural Resources (MENR), on “Preparation of National Adaptation Plan” was organized to deliver recommendations and possible amendments for Azerbaijani legislation on effectively tackling the impacts of climate change.
- The Project team in collaboration with the Ministry of Ecology and Natural Resources and the Ministry of Agriculture, organized a series of training sessions on “Climate change adaptation in agriculture” to discuss climate impacts and Azerbaijan’s agricultural problems with the local communities.
- In collaboration with the Ministry of Ecology and Natural Resources, the NAP project team held three study tours for Azerbaijan’s government representatives, with a special focus on climate change impacts on the vulnerable sectors.
- The Projects team delivered modern equipment to the Situation Center under the National Hydrometeorological Service.
- In collaboration with the Ministry of Ecology and Natural Resources, the NAP project team organized three study tours for Azerbaijan’s government representatives, with a special focus on climate change impacts on the vulnerable sectors.
- The NAP project team held the School Symposium on Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation measures for schoolchildren in April 2023. The symposium provided a platform for high school students to showcase their research projects on climate change mitigation and adaptation measures.
- NAP project team has recently organized a study tour for Azerbaijani government representatives, in partnership with the Ministry of Ecology and Natural Resources. Focused on climate change impacts in vulnerable sectors, the tour aimed to educate government officials on effective adaptation practices, particularly in regions facing heightened vulnerability.
Outcome 1: Improved data availability, access, and sharing for decision making.
Outcome 2: Enhanced institutional and technical capacity for climate change adaptation in water, agricultural and coastal areas.
Outcome 3: Increased mainstreaming of climate change adaptation considerations into planning at national, regional, local levels in priority sectors.
UNDP Press release: EU & UNDP keep taking actions to address climate change (2023)
Report.az: UNDP ready to support Azerbaijan’s efforts to combat consequences of climate change (2023)
Azerbaycan24: UNDP ready to support Azerbaijan’s efforts to combat consequences of climate change (2023) Also available in Azerbaijani and Russian.
Video: AzTv on YouTube (in Azerbaijani) (2023)
Knowledge competition dedicated to the World Environment Day was held (2022)
Azerbaijan marks the start of the National Adaptation Plan process for climate change resilience (2021)
Issues related to climate change adaptation plan were discussed (2021)
Issues related to climate change adaptation plan were discussed in ADAU (2021)
Coverage on social media
UNDP Project team collaboration with the Ministry of Ecology and Natural Resources, held three study tours for Azerbaijan’s government representatives on Facebook, X and Instagram.
UNDP organized a study tour for Azerbaijani government representatives, in partnership with the Ministry of Ecology and Natural Resources (Media coverage from Reportyor.za)
The Projects team delivered modern equipment to the Situation Center under the National Hydrometeorological Service on Facebook and X (2023).
Training in Guba and Khachmaz on Facebook, X and Instagram (2023).
Training in Salyan and Neftchala on Facebook, X and Instagram (2023).
Training in Lankaran on Facebook, X and Instagram (2023).
Training in Nakhchivan and Sharur on Facebook, X and Instagram (2023).
A workshop with UNDP and the Ministry of Ecology and Natural Resources (MENR), on “Preparation of National Adaptation Plan” was organized to deliver recommendations and possible amendments for Azerbaijani legislation on effectively tackling the impacts of climate change and featured on Facebook, X and Instagram.


GCF National Adaptation Plan project in Bhutan
Climate change is expected to bring a raft of changes to Bhutan, including long-term impacts such as rising average temperatures, reduced dry-season precipitation coupled with increased wet-season precipitation, intensified rainfall events, erratic rainfall patterns, and altered monsoon timings. Additionally, the country faces heightened risks of hydro-meteorological and geological disasters, including glacial lake outburst floods (GLOFs), landslides, earthquakes, river erosion, flash floods, windstorms, and forest fires due to climate-related factors.
The hydropower, agriculture, and tourism sectors, collectively contributing nearly a quarter of GDP in Bhutan, are significantly vulnerable to climate variability and natural hazards. In response, this project, supported by the Green Climate Fund (GCF), is dedicated to assisting the Royal Government of Bhutan in further advancing its cross-sectoral National Adaptation Plan process. The project's primary goal is to reduce vulnerability to climate change impacts by enhancing adaptive capacity and resilience. It seeks to facilitate the coherent integration of climate change adaptation into new and existing policies, programs, and activities, especially within development planning processes and strategies across various sectors and at different levels. This includes establishing a robust monitoring and evaluation system for effective implementation.
Despite significant socio-economic progress, Bhutan faces the potential reversal of gains due to the adverse impacts of climate change. Bhutan initiated its National Adaptation Plan (NAP) process in 2015, building on the 2012 National Adaptation Programme of Action (NAPA). The NAP project aims to align with Bhutan’s Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC) by accelerating medium- to long-term adaptation efforts, focusing on priority sectors, such as water resources. In addition, the project seeks to enhance Bhutan's NAP process by addressing challenges related to coordination, learning, awareness, technical capacity, systematic identification of adaptation options, and monitoring and evaluation.
National-level outcomes involve enhanced coordination, knowledge management, technical capacity for climate scenarios, vulnerability assessments, appraised and prioritized adaptation options, and the formulation of the NAP with capacity for implementation and monitoring established. These outcomes include both a comprehensive component on water resources and activities across other climate-sensitive sectors in Bhutan. Barriers to adaptation planning in Bhutan are being identified and addressed through the formulation of the NAP, while institutional frameworks and systems are being strengthened to enable long-term decision-making for climate change adaptation.
This initiative, led by the National Environment Commission Secretariat (NEC) in collaboration with various partners, builds on existing coordination efforts with UNDP and past adaptation projects, such as the GCF Readiness and Preparatory Support project “Strengthening the Capacity of NDA to access resources from the Green Climate Fund.” Mandated by Bhutan's environmental protection and water acts, the NEC’s central role is to ensure synergy with ongoing activities and prioritize adaptation options.
Project Updates
The NAP project has achieved significant milestones, including the successful publication of Bhutan’s NAP by the UNFCCC in September 2023, marked by strong ownership from the NEC and effective guidance from the Project Board and Technical Working Group. Additionally, the submitted NAP serves as Bhutan’s Adaptation Communication under the Paris Agreement. The NAP draft was presented to officials from all 20 districts, central-level agencies, development partners, civil society, private sector, and academia. A NAP implementation progress report was also produced aiming to inform the government, public, and international community about Bhutan's advancements in climate change adaptation.
The objectives of Bhutan’s NAP process are to:
1. Ensure a continuous, progressive, and iterative process to assess the vulnerability and adaptation needs across all sectors and levels in Bhutan recognising the special needs of vulnerable groups through the National Adaptation Plan process.
2. Promote the integration of climate change adaptation planning and implementation of adaptation actions into national and local level plans where possible.
3. Enhance the climate information and knowledge system to support a long-term, iterative process of adaptation planning and implementation.
4. Assess progress in adaptation including measurement of resilience and to climate change.
Project activities have made significant strides in establishing institutional arrangements, stakeholder mapping, and drafting NAP protocols and guidelines. Bhutan has successfully conducted capacity assessments, participated in global events, and developed data management protocols and a climate platform. Activities like stocktaking of climate information, vulnerability analyses, and sector-specific training programs have contributed to increased awareness and improved capacity. Notably, climate training sessions were conducted for mid-level civil servants in all 20 districts and 205 local governments and a report on climate change vulnerability analysis and mapping was compiled to evaluate vulnerable regions.
The NAP has actively incorporated insights from past vulnerability assessments, ensuring a thorough understanding of sector-specific vulnerabilities across Bhutan, including those from the Third National Communication (TNC) to the UNFCCC and various sectoral reports. This has supported sector prioritization and climate risk assessments on agriculture, health, forests and biodiversity, energy, and water resources. This includes a comprehensive assessment of groundwater in Sarpang District and preparations for the GEF-LDCF Urban Resilience Project, with a focus on Thimpu and Paro areas, addressing a mix of hard and soft adaptation priorities outlined in the NAP. Three key proposals have concentrated on green infrastructure for Thimphu City, web-based meteorological services, and a hydrological system for flood forecasting and early warning services, further contributing to Bhutan's robust approach to adaptation planning and capacity-building initiatives.
Outcome 1: Enhanced coordination, learning and knowledge management for an iterative NAP process.
Outcome 2: Technical capacity enhanced for the generation of climate scenarios and impact assessment.
Outcome 3: Vulnerability assessments undertaken and adaptation options prioritized.
Outcome 4: NAP formulated and capacity for implementation and monitoring established.
A milestone in Bhutan’s journey to adapt to climate change
Bhutan launches a new $8.9M project to build climate resilience of its water sector
Bhutan launches its first National Adaptation Plan
Safeguarding Bhutan's water in the face of climate change
NAP Expo 2023: What we heard on scaling up implementation of...
Bhutan pursues climate resilience with National Adaptation P...
Facing climate change challenges in the Kingdom of Happiness, Bhutan
Exposure: Advancing climate adaptation in Bhutan
Bhutan's climate ambition: showcasing leadership, delivering inclusive action
Exposure: At one with nature: Towards climate-resilient people, forests and wildlife in Bhutan

Readiness for the National Adaptation Plan Process in Bosnia and Herzegovina
The project “Advance the National Adaptation Plan (NAP) process for medium-term investment planning in climate sensitive sectors in Bosnia and Herzegovina (B&H)” supported the Government of Bosnia and Herzegovina to advance the National Adaptation Plan (NAP) process and reach goals outlined in the Paris Agreement and 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. The project activities enabled the government to integrate climate change-related risks, coping strategies and opportunities into ongoing development planning and budgeting processes.
Bosnia and Herzegovina’s National Adaptation Plan (NAP) builds on the country’s Climate Change Adaptation and Low Emission Development Strategy of 2013. The strategy is based on four specific outcomes: supporting evidence-based policy development for climate change risks, vulnerabilities and opportunities; creating effective institutional and regulatory frameworks; mainstreaming climate change adaptation approaches into decision making; and effectively assigning resources and reaching implementation goals. The implementation of the strategy has slowed mainly due to lack of knowledge and institutional capacity to undertake adaptation measures.
To overcome these challenges, the project advanced adaptation planning in B&H with a focus on sectoral approaches, upgrading the knowledge base for adaptation, prioritizing adaptation interventions for the medium term, building institutional capacities for integrating climate change adaptation, and demonstrating innovative ways of financing adaptation at sub-national and local government levels. The project activities resulted in the compilation of a NAP and an implementation strategy focused on scaling-up adaptation in key sectors for the medium-term. Through the project, the Government of Bosnia-Herzegovina developed municipal-level investment financing instruments with public and private sector engagement, and built national, sub-national and sectoral capacity to integrate and mainstream risk informed planning and budgeting.
Extreme climate events in Bosnia and Herzegovina are becoming more frequent; with seven out of the past 16 years experiencing drought and frequent floods. Annual temperature increases and change of precipitation are resulting in extreme weather conditions: heat waves, waves of extreme cold, and windstorms. The economic damages are vast, especially in the water, agricultural and housing sectors. The total economic impact of the 2014 floods is estimated to have reached EUR 2.04 billion, or 15 percent of the country’s GDP in 2014.
The NAP process in Bosnia and Herzegovina was officially launched in 2016 with a national consultation that engaged sector ministries and local government units via associations of cities and municipalities in Republika Srpska and Federation of B&H. B&H has put great emphasis on climate change as one of the most significant development challenges facing the country. The importance of adaptation was clearly reflected in its National Communications to the UNFCCC and Climate Change Adaptation and Low Emission Development Strategy (CCA LEDs), adopted in 2013. This strategy is based on four specific outcomes covering climate change risks, vulnerabilities and opportunities supporting evidence-based policy development, effective institutional and regulatory framework, mainstreaming CCA approaches into decision making, and effective resourcing with timely and effective implementation. However, its implementation has slowed mainly due to lack of knowledge and institutional capacity to attract finances and undertake adaptation measures.
The main identified barriers are:
- Limited institutional capacities and weak vertical and horizontal coordination for adaptation planning and implementation caused by complex administrative structure and top-down approach, limited stakeholders’ participation in B&H strategic planning for adaptation, inadequate level of technical knowledge on climate change adaptation of staff in sectoral ministries, limited training on climate change issues and low capacity to monitor, forecast, archive, analyse, communicate, and use climate risks and impacts for sectors.
- Limited climate Information to support integration of climate change into planning and budgeting due to limited scientific data and information on climate impacts and vulnerability assessments, limited knowledge of current climate variability, and a lack of systematic information on environmental protection.
- Alternative sources of finance, including innovative funds are not optimized as neither climate change adaptation, nor disaster-risk reduction (DRR) activities are included in budgeting on any level (municipal, cantonal, entity), and effective finance plan for securing adequate funds from a range of sources for adaptation does not exist.
The key results of the project include:
- An institutional framework to coordinate adaptation processes was established. The framework is based on four levels (NDA, nominated institutional coordinators, nominated interagency working group, and formed multi-disciplinary NAP drafting team).
- The first BiH NAP document was drafted identifying most vulnerable sectors and necessary adaptation actions in agriculture, water management, biodiversity, forestry, human health and tourism, with planned actions estimated over US$4.2 billion. Information on climate change impact and scenarios have been upgraded and vulnerability assessments have been completed for the most vulnerable sectors agriculture and water. The NAP document is currently under adoption at the state level.
- The Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) for horizontal and vertical institutional cooperation on climate data exchange as well as the corresponding M&E framework have been adopted as part of the NAP document. The SOPs will enable cross-sectoral climate data/information exchange to support an effective monitoring and evaluation (M&E) framework, track implementation and assess the effectiveness of adaptation actions taken to enable regular updates of the NAP.
- The Project supported adjustments to the regulatory framework necessary for successful implementation of climate change adaptation activities in the country and for meeting B&H’s obligations to the EU and the UNFCCC. This included amendments to the Law on Environment and development of strategic documents related to flood risk management to achieve alignment with the EU Approximation.
- The NAP Communication Strategy has been developed and implemented leading to the development of numerous communication products to increase knowledge and awareness on adaptation processes including a presentation at the COP 26. Project stakeholders are particularly proud of the Photo Essay on adaptation activities and potential for actions in B&H cities, which was also shared by the GCF.
- Studies on the socio-economic impacts of climate change on hydro-energy potential for two river basins (Trebisnjica and Vrbas) were undertaken, as well as a Study on socio-economic impacts of climate change on agriculture in one of most productive agricultural areas within the Sava Basin. These studies constitute the basis for informing planning and implementation of adaptation actions in water management and agriculture sectors.
- Studies assessing risks of urban torrential waters were conducted in two pilot cities (Tuzla and Banja Luka) and adaptation options were developed to improve adaptation planning in local communities.
- Trainings were conducted to build capacity of over 900 government staff for assessment, prioritization, and implementation of climate change adaptation actions as well as for development of reporting, monitoring and review mechanisms.
- Climate change data management system has been designed for the first time in B&H to enable climate data collection, exchange and assessment. The Platform is based on agreed SOP and the corresponding M&E framework will enable regular update of the NAP and other climate reports, tracking of climate data trends, implemented adaptation actions and its effects.
- Finance mechanisms, tools, and new financing approaches for adaptation finance are developed in four municipalities (Laktasi, Zenica, Sanski Most and Trebinje) to enhance adaptation investments at the local level. All four municipalities have developed and adopted their local Climate adaptation finance strategies and investment plans, developed project concepts, and were trained on adaptation finance mechanisms, benefiting over 320 participants from the four pilot municipalities.
- The Project developed two GCF Project Concept Notes (for water and agriculture sectors as the most vulnerable to climate change) and prepared the first Climate Adaptation Finance Strategy at the country level.
Outcome 1: Effective national adaptation coordination system established to drive the NAP process
Outcome 2: Capacity for climate vulnerability assessments, development of socio-economic scenarios strengthened, and adaptation options prioritized for two key sectors
Outcome 3: Innovative financing strategy for adaptation investments developed and tested in four to five selected municipalities
Exposure story: A race against nature (2019)
Exposure story: Giving trees (2019)
Exposure story: Fixing farming (2019)
Exposure story: Managing risk (2019)
Choosing peaches over apples (2021)
True Value (2021)
The Peak of Resilience (2021)
Climate change academy trainings held (2021)
Changing what we eat to help the planet (2021)
Exposure story: Financing for survival (2022)
Exposure story: Cities at the crossroads (2022)
NAP Bulletin PDF (2022)
NAP Bulletin PDF (2021)
U Tesliću održan okrugli sto na temu prilagođavanja klimatskim promjenama u Bosni i Hercegovini (2022)

Readiness for the National Adaptation Plan Process in Ecuador
Ecuador faces significant development challenges due to prevailing social, economic, and environmental conditions. The country’s vulnerability to the impacts of climate change, coupled with limited conditions for effectively integrating climate change adaptation into policies and development plans at various levels, poses a significant obstacle to progress.
Anticipated impacts include biodiversity loss, water system susceptibility, agricultural production reduction, public health challenges, and risks to infrastructure and human settlements. Climate change also exacerbates existing inequalities, especially impacting women in productive activities, and contributes to gender-based violence. Addressing these challenges is essential for Ecuador’s sustainable development and resilience.
With the support of the ‘Green Climate Fund Readiness and Preparatory Support for National Adaptation Plan in Ecuador’ project, the Government of Ecuador developed a National Adaptation Plan (NAP) constituting the basis for adaptation management at the national level, in accordance with the National Climate Change Strategy.
Development methodologies, tools, indicators, policies, capacity-building programs and studies were foreseen to create the enabling conditions for the reduction of vulnerability and climate risk in six sectors prioritized for adaptation: Water Heritage; Food Sovereignty, Agriculture, Livestock, Aquaculture and Fisheries; Natural Heritage; Health; Productive and Strategic Sectors; and Human Settlements, as well as new or ongoing programs and projects in those sectors.
Aligned with Ecuador’s Constitution and National Development Plan, the project addressed gaps and needs identified during the NAP proposal phase. It followed the guidance of the Least Developed Countries Expert Group (LEG) Technical Guidelines on NAP, focusing on improving climate projections, enhancing institutional capacities, providing training, designing measurement and verification mechanisms, and formulating strategies for financing and sustainability. The project, implemented by UNDP with the Ministry of Environment as the National Designated Authority (NDA), aimed to facilitate the integration of climate change adaptation into development planning at various levels.
The National Adaptation Plan Project in Ecuador (PLANACC) was aligned with the Constitution of Ecuador, reflecting the state's commitment to adopting measures in response to climate change and protecting populations at risk. The project also aligned with the National Strategy for Climate Change 2012-2025 and Ecuador’s Nationally Determined Contribution (2020-2025). Likewise, the Organic Code of the Environment (2018) and its Regulations (2019) determined the National Adaptation Plan (NAP) as a key instrument for climate action that enables the implementation of the National Climate Change Strategy 2012-2025.
In addition to the implementing partner, the Ministry of Environment, Water and Ecological Transition, project partners included the National Planning Secretariat and the sectoral ministries providing technical and political support related to development planning.
The PLANACC Project served as the instrument for creating the necessary conditions for climate change adaptation in the country, leading to the formulation of the NAP as both a public policy document and a management tool.
The project enabled the Government of Ecuador to contribute to the creation and strengthening of technical capacities (individual and institutional) to facilitate the integration of climate change adaptation into the central and local government's development planning and budget processes. The resources have also enabled the generation of climate information with better resolution and scale, as well as assessments of vulnerability and climate risks at sectoral, territorial, and local levels. In addition, the funds allowed for the design of technical tools and instruments (guidelines, standards, strategies, etc.) to guide the integration of climate change adaptation into development planning and enable the dissemination of results. The project also supported the formulation of financing strategies.
Key results:
The project focused on generating technical information and creating the enabling conditions that allowed for the design of the National Adaptation Plan, while also strengthening the institutional capacities of sectoral entities and local governments on adaptation management, as listed below. The NAP (2023-2027) was published by the UNFCCC in March 2023.
Datasets:
- Updated national climate projections and other relevant climate studies.
- Backfilling, updating, and homogenization of official hydrometeorological data.
- Generation of lines and sub-lines of research on climate change (as part of a National Research Agenda).
- Numerical model of the wave dynamics on the Ecuadorian coast.
Guidelines and technical studies:
- NAP (2023-2027) submitted and approved at the national level.
- Six sectoral climate risk analyses (one for each prioritized adaptation sector).
- Portfolio of conservation and recovery practices for rural production land that are resilient to climate change.
- Several guidelines to integrate climate change adaptation into development planning processes, including risk management in Human Settlements.
- Methodologies for sectoral climate risk assessments, applying impact modeling for the identification of biophysical impacts.
- Design and implementation of the methodology for the adaptation component of the 1st NDC Implementation Plan.
Political instruments:
- Integration of the climate change adaptation variable into Ecuador's Wetlands Action Plan
- Update of the management plan for the Ecological Reserve “Los Ilinizas”, including the variable of adaptation to climate change.
- Design of the implementation strategy for prioritized adaptation actions as part of the NDC Implementation Plan- adaptation component.
- Generation of technical, scientific, and regulatory tools & instruments, useful for the CCA management.
Capacity Building Products and Processes:
- Design of a Toolbox to integrate climate change into development plans and territorial planning at subnational level and complementary training program, training more than 1000.
- Design of a MOOC about fire management and climate change adaptation and conducted complementary training workshops.
- Conducted workshops on climate migration and its impact on women and children: needs, challenges, and recommendations for action.
- Implementation of virtual tools and face-to-face training courses to strengthen professional skills of 1,200 technicians.
- Synergies created and technical support provided to national and regional climate change projects.
- Provision of technical assistance addressed to public research institutes & universities (INOCAR, INAMHI and IKIAM)./li>
Gender-responsive instruments:
- Development of a Wikipedia on gender and climate change adaptation (included in the Adaptation platform).
- Database of good adaptation practices with a gender perspective.
- Inventory of shortcomings and gaps of the social, economic, and environmental information using a gender-responsive focus to prepare assessments of climate risk in the prioritized sectors for climate change adaptation.
- Provision of technical assistance and training for integrating gender approach in adaptation processes.
Communication:
- Creation of the first virtual adaptation repository platform (including newsletters, courses, information on initiatives, and NAP data).
- Communication and Awareness-Raising Strategy to integrate climate change adaptation into development planning processes.
- Generation of recreational tools for raising awareness and training girls, boys, and adolescents on CCA.
- Development of a contest of illustrated stories for children on climate change and implementation of an exhibition at the Interactive Science Museum. Until 02/02/2023 more than 15,000 visitors were received.
Lessons learned
The NAP process in Ecuador yielded valuable lessons and best practices. The utilization of innovative biophysical impact models for sectoral climate risk analyses proved to be a complex and time-consuming endeavor. Moreover, the socialization and participatory construction of the NAP demanded meticulous planning, development, and adherence to official communication and dissemination guidelines.
Adaptation planning, based on the outcomes of comprehensive climate risk analyses, ensured the availability of reliable information for decision-makers and technicians. Crucially, the empowerment of the National Designated Authority (NDA), the Ministry of Environment, played a pivotal role in sustaining the continuity of the NAP process. Actively involving relevant stakeholders not only empowered them with the results achieved during the NAP formulation phase but also fostered commitment to planned adaptation actions.
Furthermore, the generation of studies, regulations, and technical tools for CCA needs alignment with national, sectoral, and local needs, with an emphasis on flexibility to accommodate changes in regulations, sectoral policies, and the composition of institutional technical teams.
Output 1: National mandate, strategy and steering mechanisms are in place and gaps are assessed and addressed.
Output 2: Preparatory elements for the NAP are in place to develop a knowledge base and formulate the NAP.
Output 3: NAP implementation is facilitated.
Output 4: Mechanisms for reporting, monitoring and review of NAPs and adaptation progress in place.
Output 5: Funding strategy for the NAP and climate change adaptation is available.
Ministerio del Ambiente presentó oficialmente el Plan Nacional de Adaptación al Cambio Climático (2023,Ministry of Environment, Water, and transition)
Los gobiernos provinciales aportan a la construcción del Plan Nacional de Adaptación al Cambio Climático (2023, ConGoPE)
Scientific dissemination, a key pillar for understanding climate change
Updating climate projections, a comprehensive process
Adaptation to climate change is possible by promoting capacity building processes
The country's higher education has a new master's degree in climate change
The country's higher education has a new master's degree in climate change
Talking about climate change from different perspectives of communication
Climate migration, time to join forces
Advancing adaptation and gender equality in Ecuador (also on Exposure)
Development of a virtual skills course focused on adaptation to climate change
Ecuador presented the results of the report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
Updating climate projections, a comprehensive process
Ministry promotes illustrated story contest for children on climate change
Technicians are trained in numerical model to predict floods on the coasts of Ecuador
Ministry presented the first digital platform for adaptation to climate change in the country


Formulation and Advancement of the National Adaptation Plans Process of Egypt
The project is advancing the development of Egypt’s National Adaptation Plan (NAP) with the goal of decreasing vulnerability to climate change. This NAP process is helping Egypt to build climate resilience by improving institutional and technical capacity for climate change adaptation planning, evaluating climate risks, determining adaptation priorities, integrating adaptation into national and sectoral planning and budgeting, and increasing investment in adaptation actions.
The project is expected to equip the Government and relevant ministries with information on climate risks and vulnerabilities and priority adaptation areas, as well as help the government to implement effective adaptation planning.
The project “Formulation and Advancement of the National Adaptation Plans Process of Egypt” started in July 2021 with the main objective of decreasing Egypt’s vulnerability to climate change by advancing the NAP development. The NAP project is helping the country build climate resilience by improving institutional and technical capacity for climate change adaptation planning, examining climate risks, determining adaptation priorities, integrating adaptation into national and sectoral planning and budgeting, and increasing investment in adaptation actions.
Climate change impacts in Egypt include the rising sea level, extreme weather events such as heat waves, flash floods, heavy precipitation, sand and dust storms, and water scarcity. These complex climate-related challenges threaten agriculture, food security, human health, and the national economy. Egypt‘s ability to respond to these impacts is challenged by low technical capacity for adaptation planning and limited information on climate risks and vulnerabilities. To address the risks, the Government of Egypt began a NAP process in May 2015, which resulted in a roadmap for advancing adaptation planning.
The 2017 stocktaking exercise assessed accomplishments since 2015 and identified priority interventions for the NAP process. Based on this assessment, the NAP project focuses on the following outcomes: (1) Strengthening institutional and human capacities to coordinate and manage climate change adaptation planning and implementation; (2) Developing an integrated national climate risk assessment and identifying adaptation priority areas for inclusion in a National Adaptation Plan Framework document; and (3) Mainstreaming adaptation priorities into national planning and budgeting processes.
Target outcomes will equip Egypt with the required climate risk information and understanding of priority adaptation areas to enable the government to conduct effective adaptation planning and start integrating climate adaptation into national development planning and budgeting. As a result of project activities that improve capacity and climate adaptation governance, national ministries and the Government of Egypt will be empowered to help programs and projects across national and sub-national processes be more climate risk-informed, and climate adaptation indicators will be specifically incorporated into the national development strategy “Egypt Vision 2030”.
Recent Activity
The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) hosted a training workshop as part of the FAO-UNDP SCALA program(Scaling up Climate Ambition on Land Use and Agriculture through Nationally Determined Contributions and National Adaptation Plans). The workshop focused on facilitating dialogues within the Ministry of Agriculture and the Ministry of Environment, providing skills to generate crucial information on climate impacts and solutions in agriculture. The insights are contributing to Egypt's NAP process, aligning with the national vision for 2030 and sustainable development. The SCALA program, funded by the German Federal Ministry for the Environment, Nature Conservation, Nuclear Safety and Consumer Protection (BMUV) through the International Climate Initiative (IKI), aims to integrate climate-resilient agricultural practices into NAPs and enhance capacities for effective climate risk management in Egypt.
Outcome 1: Strengthening institutional and human capacities to coordinate and manage climate change adaptation planning and implementation;
Outcome 2: Developing an integrated national climate risk assessment and identifying adaptation priority areas for inclusion in a National Adaptation Plan Framework document;
Outcome 3: Integrating adaptation priorities into national planning and budgeting processes.
SCALA supports Egypt with integrating agriculture into the National Adaptation Plan (2023)
Video: Using the power of nature to fight climate change in Egypt (2023)
NAP Inception Workshop (2023)
Egypt scales up climate adaptation actions of its agriculture, water and agrifood sectors (2022)
Egypt’s Environment Ministry signs document formulating National Adaptation Plan (2021)


Enhancing Research and Policy Linkages to Advance National Adaptation Planning in Guinea
The project helped Guinea to increase its capacity to adapt to climate change impacts by strengthening linkages between research policy, mainstreaming climate change adaptation into sectoral and local planning and budgeting, and advancing national funding mechanisms and private sector engagement. The project addressed the main barriers that were identified during an earlier stocktaking exercise, including the lack of links between research and policymaking, weak measurement, evaluation and funding mechanisms, and insufficient private sector engagement in adaptation efforts.
The main objective of the project “Enhancing research and policy linkages to advance National Adaptation Planning in Guinea” was to increase Guinea’s adaptive capacity to cope with climate change impacts. The project established research to support informed decision-making and capture opportunities that arise both from public funding and the private sector.
Guinea is experiencing negative socio-economic impacts of climate change due to its exposure to sea level rise, droughts, and flooding. Its Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC), submitted in 2015 and revised in 2021, outlines climate change adaptation priorities, such as the preservation and restoration of water resources, protection of ecosystems particularly in coastal zones, and ensuring food security of rural communities.
Based on stakeholder consultations and stocktaking conducted in 2016 and 2018, the main barriers to climate change adaptation mainstreaming and financing were identified as (1) the absence of links connecting research to policy to inform decision-making processes; (2) weaknesses in and/or fragmentation of existing coordination, monitoring & evaluation (M&E), and funding mechanisms; (3) the absence of adaptation in the Planning-Programming-Budgeting-Monitoring and Evaluation (PPBSE) procedures; and (4) lack of private sector involvement in the adaptation landscape.
The project aims to remove these barriers by achieving the following objectives under the three main outcomes:
1. Research-policy linkages and knowledgebase are strengthened to inform adaptation planning and decision-making:
- Establish research-policy linkages to support the NAP (National Adaptation Plan) formulation and implementation;
- Develop a climate risks and vulnerability evidence base that informs the identification and prioritization of adaptation options in the sectors of agriculture, livestock, and forestry.
2. Climate change adaptation mainstreaming is facilitated by reinforcing coordination and M&E mechanisms:
- Operationalize a sustained and suitable coordination mechanism to support mid and long-term adaptation;
- Enhance adaptation mainstreaming into sectoral and local planning and budgeting;
- Establish adaptation M&E mechanisms in adherence with the existing national M&E system.
3. A national funding mechanism and private sector engagement are expanded to support adaptation financing:
- Support the Environmental Safeguard Fund (FSE) mechanism to raise awareness on funding sources and expand mandate for the financing of adaptation actions;
- Enhance the mining sector’s engagement on adaptation and climate financing.
Furthermore, a follow-up project was proposed to fill gaps identified through this phase and develop Guinea’s NAP document. The results of the current project have informed the proposal, consolidating existing climate risks and vulnerability assessments and prioritization of adaptation options in the priority sectors of agriculture, livestock, forestry, coastal and water resources. The planned second phase will further consider promoting sustainable cities, clean cities, and blue economy for which the national strategy is currently being developed.
In addition to the main project implementing partner, the Ministry of Environment, Water and Forests, other project partners included the Ministry of Economy and Finance (MEF), National Directorate of the Environment (DNE)/current National Directorate of Pollution, Nuisance and Climate Change (DNPNCC), sectoral Strategy and Development Offices (BSD), the various research institutes, the Center for Observation, Monitoring and Environmental Information (COSIE), the National Institute of Statistics (INS), the Fund for the Environment and Natural Capital (FECN), the Bauxite Environment Network (REB), Guinea-Ecology, civil society organizations and municipalities.
Project results
Activities under Outcome 1 led to the development and validation of key documents, including those for the Research-Policy Working Group (RPWG), Environmental Research and Climate Change Plan, and Updated Climate Projections Based on Appropriate Models (AR5 RCP). An interim report on vulnerability analysis in lower, middle, and upper Guinea was developed, and activities focused on setting up and running the RPWG team and prioritizing adaptation options in key sectors such as agriculture, livestock, forestry, and coastal and water resources. A Climate Risks and Vulnerability Assessment (CRVA) report was completed, including training modules used to train representatives from sectoral ministerial departments. This included strengthening the capacities of the national CRVA team to collect information on the impacts of climate change on key sectors in three of the four natural regions of Guinea. A workshop was conducted to prioritize adaptation options for key sectors.
Under Outcome 2, an operational manual was created for the National Committee on Climate Change (CNCC), featuring tools like a project monitoring tool, multi-year CNCC work plan, climate action monitoring system, management chart, and reporting system. A monitoring and evaluation framework for climate change adaptation, aligned with the national monitoring and evaluation system (DISE) of the National Plan for Economic and Social Development (PNDES), was established. Capacity-building sessions were conducted for government officials on integrating adaptation into the DISE. Additionally, studies focused on creating a sustainable coordination mechanism to support medium and long-term adaptation and updating climate models and projections, with corresponding training for managers. Data was collected and improved through a national stakeholder workshop. Furthermore, discussions with the National Institute of Statistics (INS) aimed to progress a partnership agreement for updating the statistical yearbook using the monitoring and evaluation framework. Technical guidelines were also developed to integrate climate change adaptation into sectoral planning and budgeting.
Outcome 3 focused on supporting the Environment and Natural Capital Fund (FECN) and the Bauxite Environment Network (REB). Discussions led to the finalization of terms of reference for activities, including conducting and validating a study on potential funding sources for the FECN and developing a strategic plan. The FECN mechanism was supported to raise awareness of funding sources and expand the mandate for financing adaptation actions. The project will also support the implementation of the REB 2024-2025 action plan to facilitate the private sector's commitment to adapting to climate change. Moreover, efforts were made to enhance the mining sector's engagement in adaptation and climate financing.
Outcome 1: Research-policy linkages and knowledge base are strengthened to inform adaptation planning and decision-making.
Outcome 2: Climate change adaptation mainstreaming is facilitated by reinforcing coordination and monitoring and evaluation mechanisms.
Outcome 3: A national funding mechanism and private sector engagement are expanded to increase climate change adaptation financing.
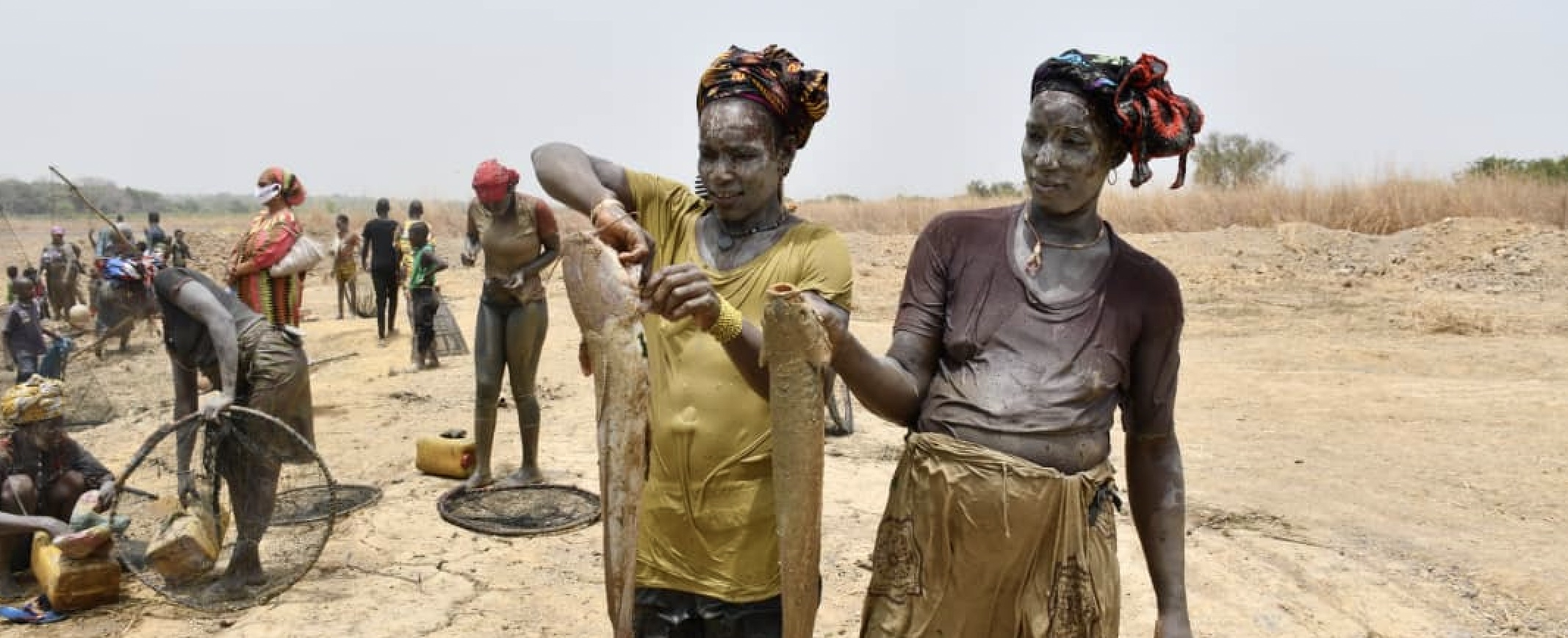
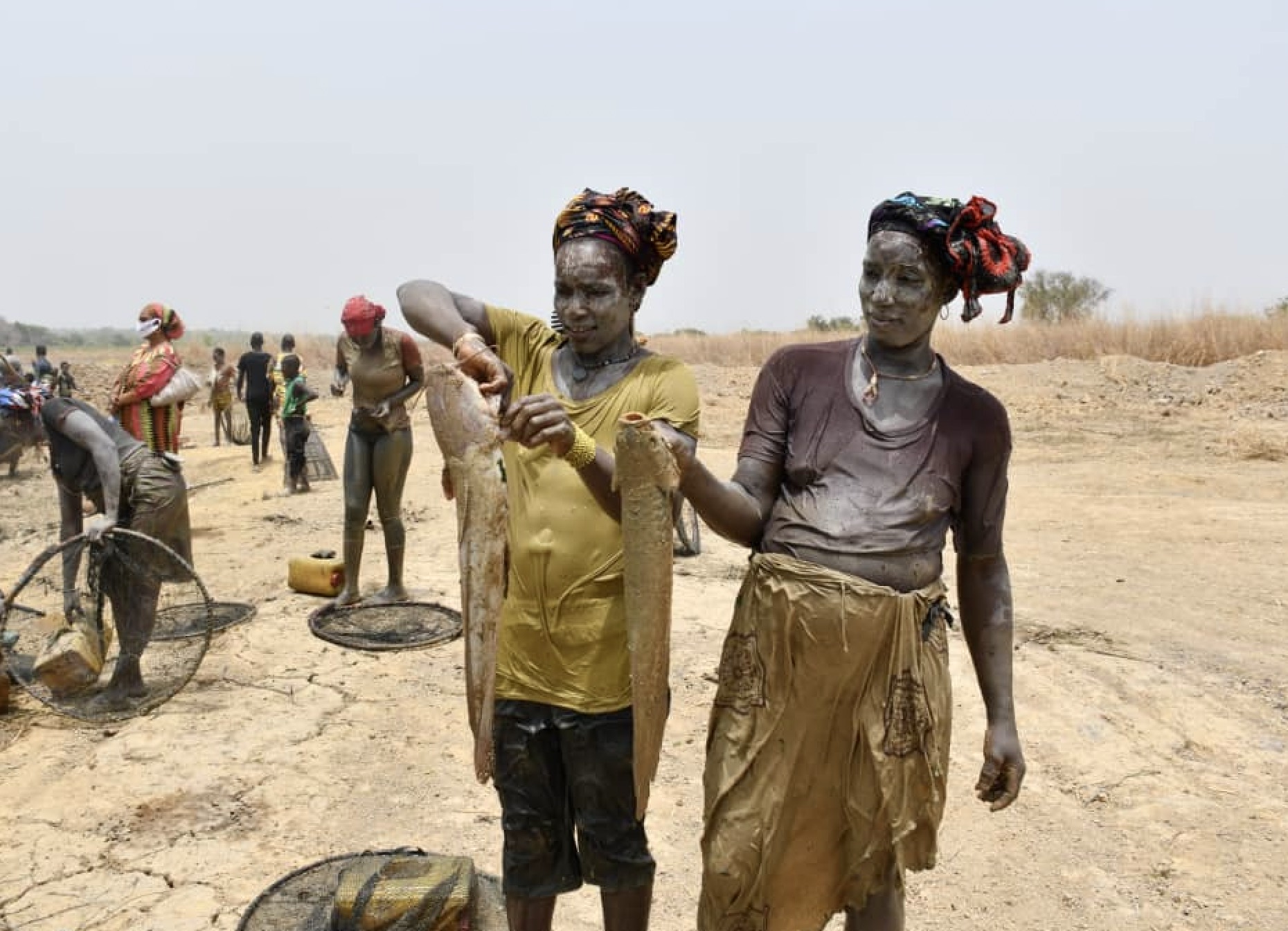


Integrating Climate Change Risks into National Development Planning Processes in Haiti
The project sought to strengthen institutional and technical capacities in Haiti to iteratively develop a National Adaptation Plan (NAP). Additionally, it aimed to integrate climate change adaptation into national and sub-national coordination, planning, and budgeting processes. This objective was achieved by advancing existing frameworks and systems, enhancing the capacities of various stakeholders to effectively contribute to the process, and establishing a mechanism to sustain the NAP process beyond this project.
Funded by the Green Climate Fund (GCF) Readiness Programme, the "Integrating climate change risks into national development planning processes in Haiti" project supported the Government of Haiti in strengthening institutional and technical capacities for iterative development of the National Adaptation Plan (NAP). This included integrating climate change adaptation into national planning and budgeting processes.
The project built on lessons from the National Adaptation Programme of Action (NAPA) implementation, as well as complementary activities currently underway in Haiti to avoid duplication of efforts. By integrating climate change adaptation into development plans, the project sought to align inclusive climate change adaptation priorities with the country’s visionary Strategic Development Plan (PSDH), National Land Use Plan (SNAT) and Disaster Risk Reduction Plan and Strategy.
As the only Least Developed Country (LDC) in the Caribbean region, Haiti’s primary economic sectors (i.e., agriculture, forestry, and fishing) are heavily affected by climatic events. As of 2023, nearly 59 percent of Haiti’s population lives below the poverty line, many of those people living in extreme poverty. According to the World Bank’s Climate Change Overview Country Summary (2022), political violence, economic imbalance, and population pressure have led to extreme environmental degradation in Haiti, with an estimated 98 percent of forests cleared for fuel. These destabilizing forces have left most Haitians extremely vulnerable to natural hazards.
Haiti has embarked on many initiatives to strengthen its resilience to climate change. However, fragmented policies and data, weak technical capacity, and inadequate climate financing, among others, have hampered the country’s efforts to plan effectively and iteratively for medium-to-long-term climate risks in its development planning and budgeting.
The project was informed by stakeholder consultations and stocktaking of existing initiatives, policies, and strategies in Haiti that were conducted by the National Adaptation Plan Global Support Programme in 2017, which resulted in an action plan to implement the NAP. The Stocktaking Report highlighted limitations and gaps, including insufficient technical and institutional capacity to effectively coordinate and implement climate change adaptation measures, scattered data and information-sharing on climate change impacts and adaptation interventions, limited capacity to monitor climate change adaptation and inform policies, and inadequate budget allocations. These served as the basis for the project activities that were later confirmed by stakeholders.
The project is expected to deliver the following results under the three key outcomes:
- Capacities of the Technical Working Group, particularly MDE (Ministry of Environment) and MCPE (Ministry of Planning), to steer the climate change coordination and integration process are developed;
- Institutional barriers to the integration of climate change into development planning and policies are reviewed and key stakeholders are sensitized to climate change adaptation and development linkages;
- Mechanisms for regularly updating and reviewing adaptation are strengthened and feed into the iterative adaptation planning process;
- Haiti's National Adaptation Plan is developed;
- A system for economic analysis and appraisal of adaptation options is established and adaptation priority interventions are integrated into the SNAT, PSDH and PNGRD;
- Universities and educational institutions are capacitated to support adaptation initiatives and the NAP process;
- Financing and Investment Strategy for the NAP is developed through a gender responsive consultative process;
- Private sector engagement in climate change adaptation is strengthened.
Project results
Despite socio-political challenges, the project advanced the NAP process in Haiti, focusing on enhancing national institutional capacities. The NAP was developed and validated by both the Ministry of Environment (MDE) and the Ministry of Planning (MCPE). The NAP document was presented at COP 27 in Egypt, the NAP Expo 2022 in Botswana, and at the launch of the National Committee on Climate Change (NCCC), providing platforms for experience-sharing and networking with potential partners. Subsequently, the NAP was published by UNFCCC in January 2023.
The project has produced strategic documents and tools, including a gender integration strategy, an exploratory report on private sector engagement in climate change adaptation, and a training mission for actors in planning and budgeting for adaptation. A NAP financing and investment strategy was developed through broad consultations with diverse stakeholders, including women’s organizations, while the communication strategy for the NAP process was validated and disseminated nationwide. An assessment of the regulatory framework and the vulnerabilities of priority sectors, such as health, agrobiodiversity, and water resources, was also conducted.
Other activities included technical working group meetings from sectorial ministries to strengthen capacity, ongoing training on climate information and adaptation integration, and stakeholder development planning and budgeting. Adaptation criteria were integrated into the Haiti Public Investment Program, while other efforts focused on incorporating SDG-aligned adaptation indicators into the national MRV system, creating new data layers with the Ministry of Environment, and organizing workshops on monitoring and evaluation, including a workshop on adaptation practices. Additionally, research programs for priority sectors with two Haitian universities were finalized.
Various initiatives aimed at revising strategic documents were supported, including the Nationally Determined Contributions (NDC), the development of an operational plan for the PNGRD and the reinforcement of the EIS-Haiti database for the monitoring of climate indicators, among others. Additional activities involved formulating addendums for the PSDH and SNAT, developing project concept notes, and promoting private sector participation in adaptation.
Several good practices and lessons learned from adaptation measures were compiled to promote successful approaches and were incorporated into the Environmental Information System platform. Moreover, collaboration with partners and stakeholders allowed the project to continue the implementation and validation of deliverables while developing synergies between climate change adaptation actions in the field.
Outcome 1: The coordination mechanism for multi-sectoral adaptation planning and implementation is strengthened at different levels
Outcome 2: The NAP is compiled with a strong evidence base for adaptation planning and priorities are integrated into the Strategic Development Plan and the Disaster Risk Reduction Plan and Strategy
Outcome 3: A financing framework for climate change adaptation action in the medium-to long-term is established.